
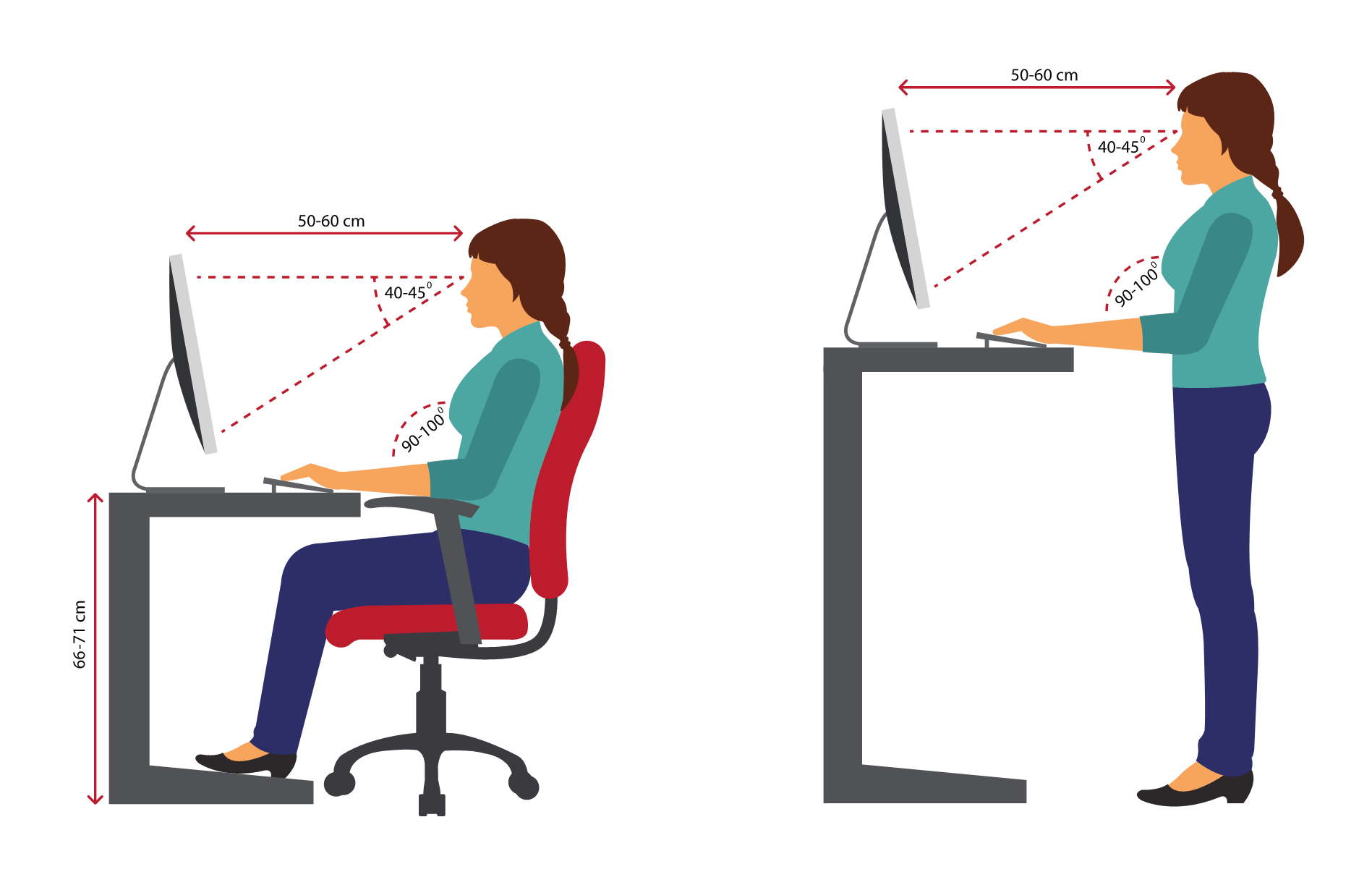
In some models the keyboard is elevated in the middle, making its 2 sides slanted, a bit like the sides of a low tent. The two sets of keys are at an angle to each other. Some people find a split keyboard useful - this type of keyboard separates the keys pressed by your right hand from those pressed by your left. If it feels comfortable, you should lower the feet at the rear of the keyboard as this reduces the height and angle of the keyboard, which helps avoid load on the shoulders and wrists. However, the keyboard should not be so far towards you that your wrists rest on the sharp edge of the desk. Putting such documents between the keyboard and the front of the desk pushes the keyboard too far back on the desk, disrupting your posture. Put reference documents either between the monitor and the keyboard or directly alongside the screen in a document holder. The keyboard should be aligned with the monitor and directly in front of you so that you don’t have to twist or rotate to use it. Your elbows should be close to your body. This means that your hands should not be bent up, down or to either side in relation to your forearms. You should be able to have your forearms close to horizontal and your wrists straight when using the keyboard.
Stand up to get items that are further away.Ī desk with a matte surface helps minimise glare. Make sure everything you need is within reach so that you don’t have to stretch for things. Your desk area should be deep enough to accommodate your monitor at the appropriate distance and to place the things you use most often directly in front of you.

Remember to rest them every 10 minutes or so by looking away into the distance. You should also adjust the monitor’s brightness to a comfortable level.Įven with these adjustments, your eye muscles can become tired when you do a lot of close work. Tilting the monitor slightly downwards can help with this. If your screen is reflecting the light, it’s worth experimenting with the overhead lights and window blinds to reduce these reflections. To avoid glare and reflections, neither you nor the monitor should directly face the window. When working at the computer, use a pair of single-vision lenses with a focal length designed for computer work.This may mean that you have to raise the keyboard and use a footrest. Raise your chair until you can view the monitor without tilting your head back.Position the monitor lower than normal to compensate for needing to look through the bottom of your lenses.If you wear bifocals, there are several ways to address this problem. This makes them tilt their head backwards, which can fatigue the muscles supporting the head. People who wear bifocals tend to look through the bottom part of the lenses to view the monitor. The top of the screen should be at eye level or just below so that you look down at a slight angle to your work.

The monitor should be roughly an arm’s length away.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/how-to-set-up-an-ergonomic-home-office-and-get-rid-of-back-pain-5080957-ADD-FINAL-GIF-1fdd2786da844722b3ff1c8d65df65bb.gif)
If your chair can’t be adjusted so that your back is straight, place a cushion between the curve of your lower back and the back of the chair. Your backbone should be straight and your shoulders back. When sitting, your knees should be about level with your hips, and the seat of your chair should not press into the back of your knees. Correctly adjusting your chair can help you maintain proper posture and take the pressure off your back.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
